Cold Chamber vs. Hot Chamber Diecasting: Key Differences
Diecasting is a widely used metal manufacturing process that allows for the mass production of complex and high-precision metal parts. The process involves injecting molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. There are two main types of diecasting machines: cold chamber diecasting machines and hot chamber diecasting machines.
While both methods share the same fundamental principle, they differ significantly in their applications, materials, and operational processes. In this article, we will explore the key differences between these two methods and why Beta Diecasting is the ideal choice for high-quality diecasting machines.
Understanding Diecasting Processes
Before diving into the differences, it is essential to understand the diecasting process. In both cold and hot chamber diecasting, a mold (die) is created to shape the final product. Molten metal is then injected into this mold under high pressure, ensuring precise shapes with excellent surface finishes. However, the way the molten metal is handled before injection is what differentiates cold and hot chamber diecasting.
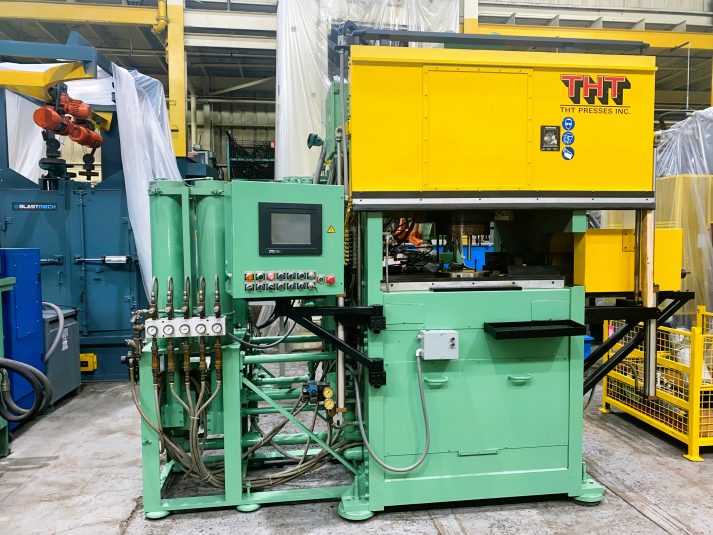
What is Cold Chamber Diecasting?
Cold chamber diecasting is a process in which molten metal is manually or automatically ladled into the shot chamber before being injected into the mold. The injection mechanism is separated from the molten metal source, which helps minimize exposure to high temperatures.
Key Features of Cold Chamber Diecasting:
- The molten metal is poured into the chamber from an external furnace.
- Suitable for high-melting-point metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys.
- The process requires longer cycle times due to the additional step of transferring the molten metal.
- Reduces corrosion of machine components since the molten metal is not in continuous contact with the injection system.
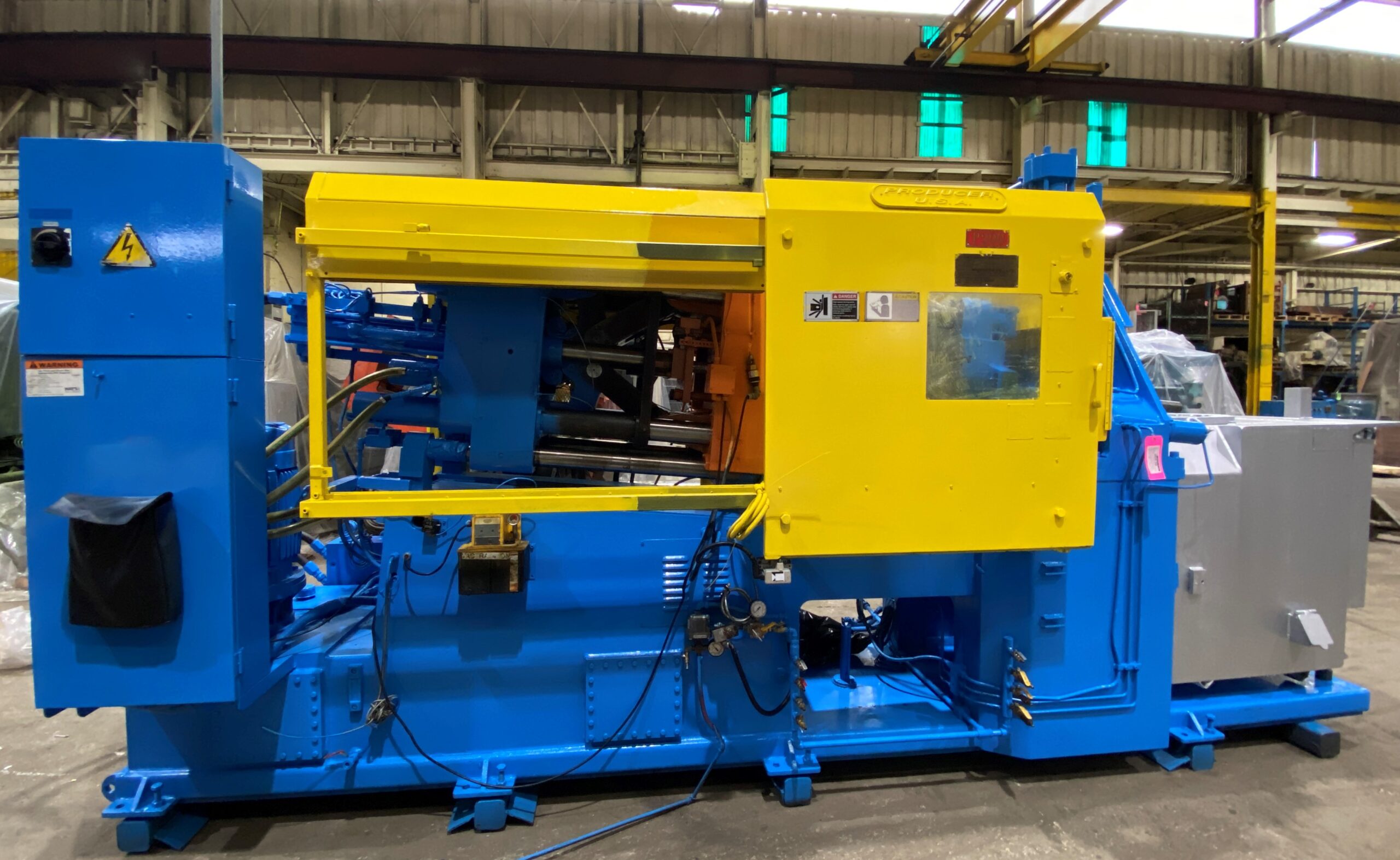
What is Hot Chamber Diecasting?
Hot chamber diecasting (also known as gooseneck diecasting) integrates the metal melting pot into the diecasting machine. The injection mechanism is submerged in the molten metal, allowing for rapid injection cycles.
Key Features of Hot Chamber Diecasting:
- The machine contains an internal furnace where the metal remains in a molten state.
- Suitable for low-melting-point metals such as zinc, tin, and lead.
- Faster cycle times as the metal is directly injected into the mold.
- The continuous exposure of machine components to molten metal increases the risk of corrosion.
Key Differences Between Cold and Hot Chamber Diecasting
1. Metal Types Used
One of the most significant differences between these two processes is the type of metals they can handle.
- Cold chamber diecasting is used for metals with high melting points, such as aluminum and copper.
- Hot chamber diecasting is ideal for metals with lower melting points, such as zinc and lead.
2. Speed and Cycle Time
- Hot chamber diecasting is much faster because the molten metal is directly available for injection, making it suitable for high-volume production.
- Cold chamber diecasting takes longer due to the additional step of transferring molten metal into the injection chamber.
3. Corrosion and Machine Durability
- Hot chamber diecasting machines are exposed to molten metal at all times, leading to higher wear and tear.
- Cold chamber diecasting machines have a lower risk of corrosion since the molten metal is introduced only during the injection process.
4. Production Efficiency
- Hot chamber diecasting allows for higher production rates and is often used for small to medium-sized components.
- Cold chamber diecasting is better suited for larger, more complex parts that require precision and durability.
5. Equipment and Cost Considerations
- Hot chamber machines are generally more compact and require less manual handling.
- Cold chamber machines require additional equipment, such as an external furnace, which can increase setup costs but offer more flexibility in metal choices.
Why Choose Beta Diecasting Machines?
For businesses looking to invest in high-quality diecasting solutions, Beta Diecasting offers industry-leading cold chamber diecasting machines and hot chamber diecasting machines designed for maximum efficiency and durability. Here’s why Beta Diecasting is the preferred choice:
1. Advanced Technology
Beta Diecasting incorporates cutting-edge technology to ensure precision, reliability, and efficiency in both cold and hot chamber diecasting machines.
2. Versatile Solutions
Whether you need a cold chamber diecasting machine for aluminum and copper or a hot chamber diecasting machine for zinc and lead, Beta Diecasting provides customizable solutions tailored to your production needs.
3. Durability and Longevity
Beta Diecasting machines are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of continuous production while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
4. Superior Customer Support
With a team of experts, Beta Diecasting ensures that clients receive top-notch support, from machine selection to installation and maintenance.
5. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Investing in a Beta Diecasting machine means improved productivity, reduced waste, and a high return on investment for your diecasting operations.
Conclusion
Both cold chamber diecasting and hot chamber diecasting play crucial roles in modern manufacturing. The choice between the two depends on the type of metal used, production speed, and durability requirements. Cold chamber diecasting machines are ideal for high-melting-point metals like aluminum, while hot chamber diecasting machines work best for low-melting-point metals like zinc. Businesses looking for reliable and efficient diecasting solutions should consider Beta Diecasting, a trusted name in diecasting machine manufacturing. Whether you need a cold chamber diecasting machine or a hot chamber diecasting machine, Beta Diecasting provides high-quality equipment designed to enhance productivity and precision in metal casting operations.